Most common elements on earth are si o sio2 silica structures are quartz crystobalite tridymite the strong si o bond leads to a strong high melting material 1710ºc si4 o2 adapted from figs.
Type of bonds that hold ceramic crystal structure.
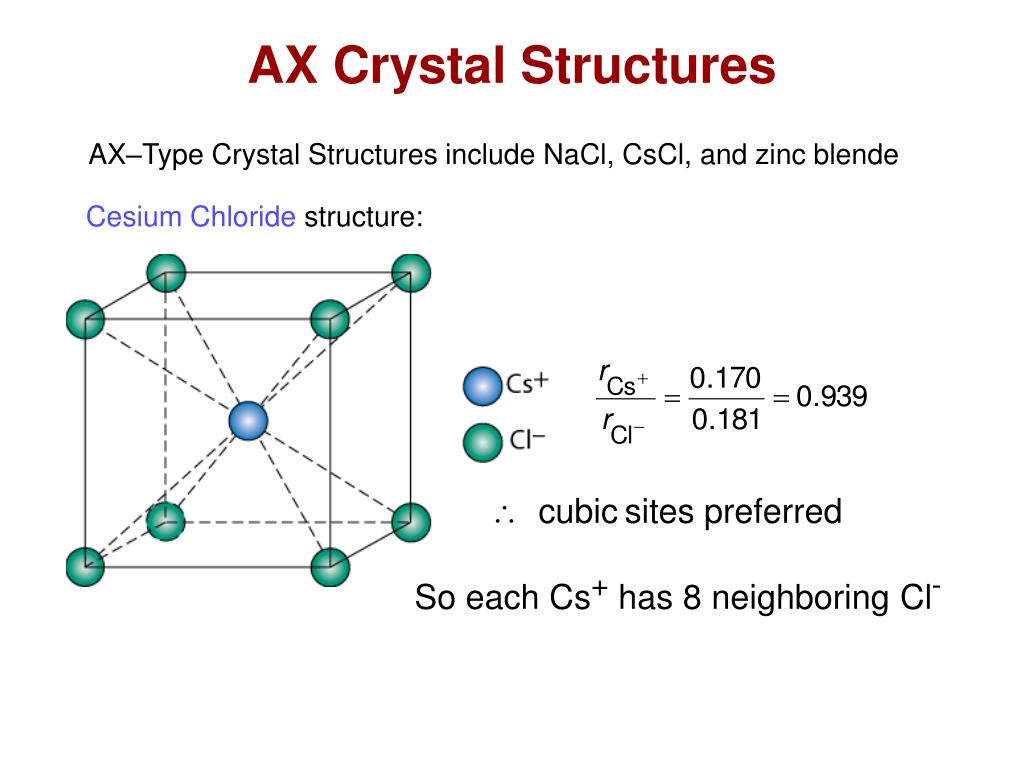
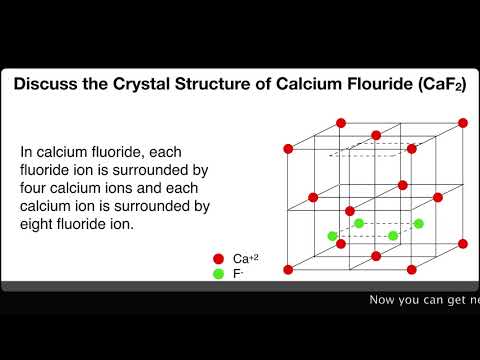
Crystal structures ceramic structure ax type crystal structures amxp type ambnxp type silicate ceramics carbon ceramic structures two or more different elements more complex than metal structures ionic and or covalent bonds a mix of ionic and covalent bonds electronegativity ionic bonds form ions.
Hydrogen bonded solids such as ice make up another category that is important in a few crystals.
The bonding of atoms together is much stronger in covalent and ionic bonding than in metallic.
Four main bonding types are discussed here.
Brittleness one kind known as an edge dislocation an extra plane of atoms can be generated in a crystal structure straining to the breaking point the bonds that hold the atoms together.
This is why ceramics generally have the following properties.
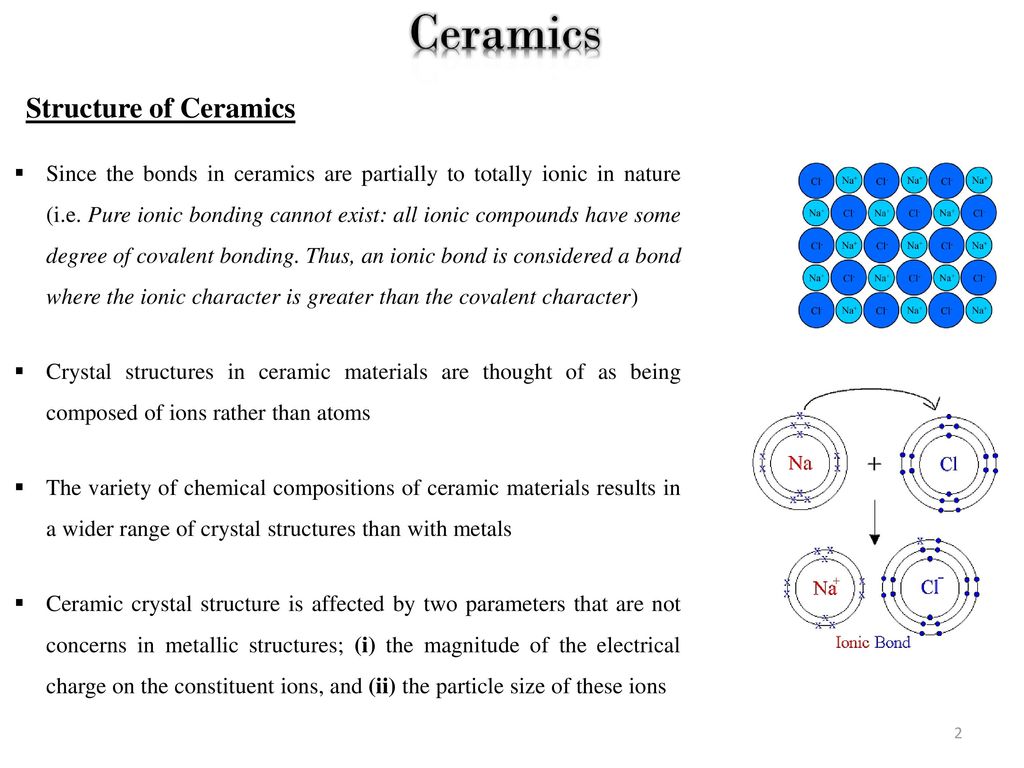
They are either ionic in character involving a transfer of bonding electrons from electropositive atoms to electronegative atoms or they are covalent in character involving orbital sharing of electrons between the constituent atoms or ions.
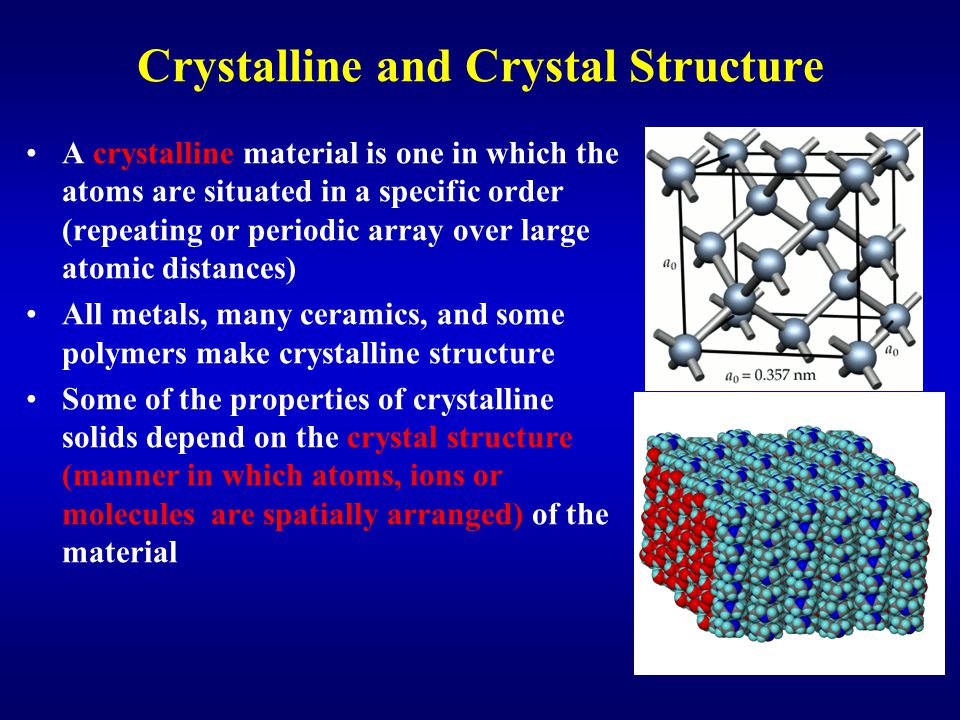
The primary difference between ceramics and other materials is the chemical bonds that hold these materials together.
The reasons for this lie in the nature of the bonds holding the crystal structure together.
Crystal crystal types of bonds.
If stress were applied to this structure it might shear along a plane where the bonds were weakest and read more.
Two types of bonds are found in ceramics.
The two most common chemical bonds for ceramic materials are covalent and ionic.
Underlying many of the properties found in ceramics are the strong primary bonds that hold the atoms together and form the ceramic material.
In ceramic composition and properties.
High hardness high compressive strength and chemical inertness.
Ionic covalent metallic and molecular.
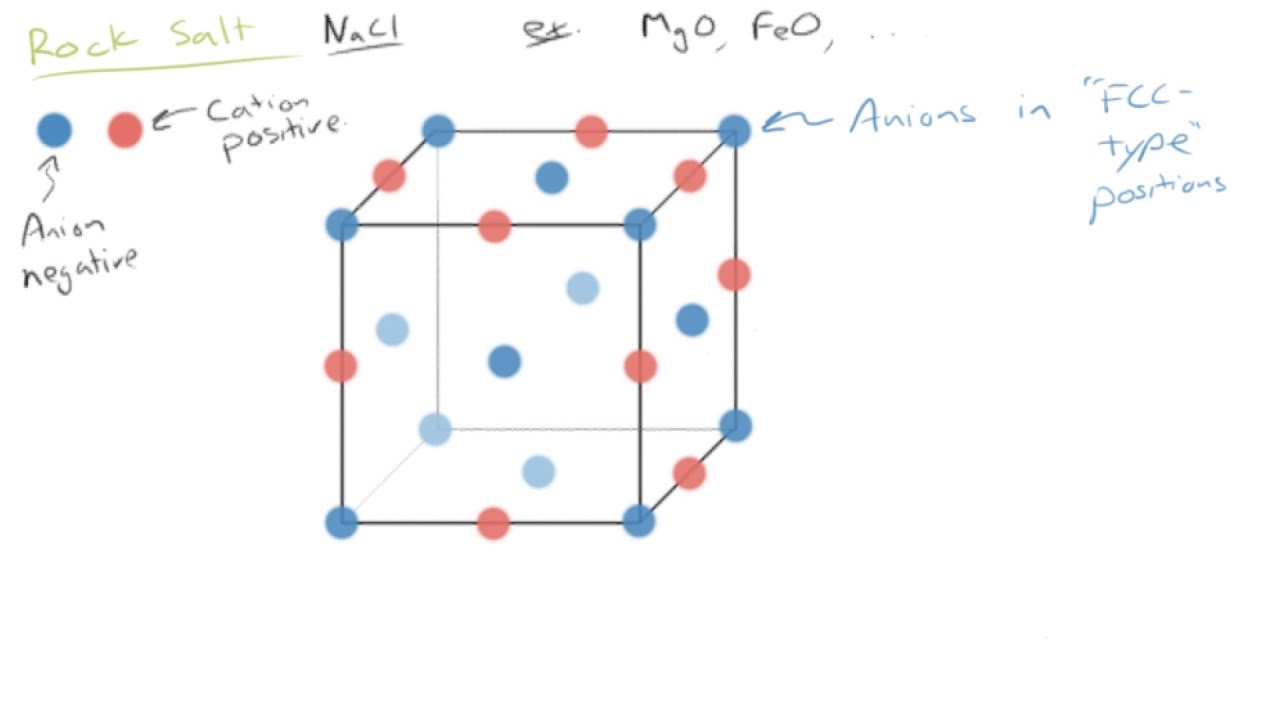
In ionically bonded ceramics some planes such as the so called 111 plane shown slicing diagonally through the rock salt structure in figure 3 top contain only one kind of ion and are therefore unbalanced in their distribution of charges.
It occurs naturally in its crystalline polymorphic.
The properties of a solid can usually be predicted from the valence and bonding preferences of its constituent atoms.
The ionic bond occurs between a metal and a nonmetal in other words two elements with very different electronegativity.
Attempting to insert such a half plane into a ceramic would not favour a stable bond unless a half plane of the oppositely charged ion was also inserted.
When they form crystals the strong force of attraction between ions of opposite charge in the planes of ions make it difficult for one plane to slip past another.
Aluminium oxide is a chemical compound of aluminium and oxygen with the chemical formula al 2 o 3 it is the most commonly occurring of several aluminium oxides and specifically identified as aluminium iii oxide it is commonly called alumina and may also be called aloxide aloxite or alundum depending on particular forms or applications.